Many patients delay dentistry for understandable reasons: cost, timing, fear, or simply feeling “nothing hurts yet.”
But dental diseases progress silently, and once they reach a certain stage, they often become more complex, more expensive, and require more time to treat.
This article explains, in simple and scientific terms, what typically happens in the mouth when common dental issues are not treated early. The goal is not to alarm, but to provide clear information so you can make informed decisions about your oral health.
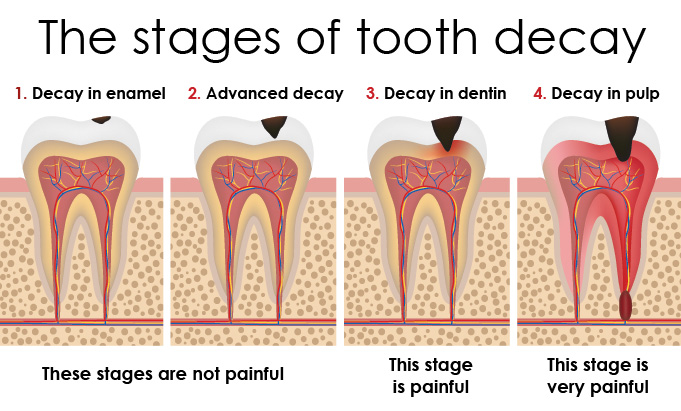
1. Early Stage (Enamel Only)
Decay begins in the enamel, the outer mineral layer.
At this stage, it may be reversible through remineralising treatments and hygiene improvements.
Why it matters:
Once the cavity enters the dentine, reversal is no longer possible.
2. Middle Stage (Dentine Involvement)
When decay reaches dentine, the tooth becomes softer and bacteria spread more rapidly.
Consequences of not treating:
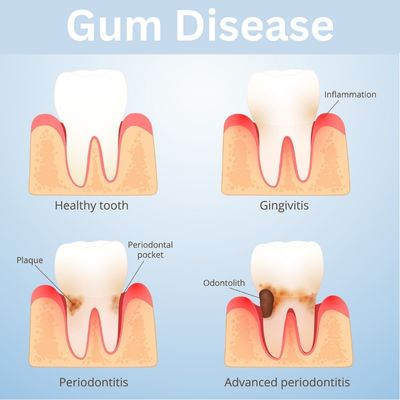
Gingivitis
Early gum inflammation is reversible with professional cleaning and home care.
Periodontitis (Bone Loss)
If plaque and calculus remain long enough, gums detach and bone begins to resorb.
If untreated:
Research has linked periodontitis to higher risks of cardiovascular disease, diabetes complications, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
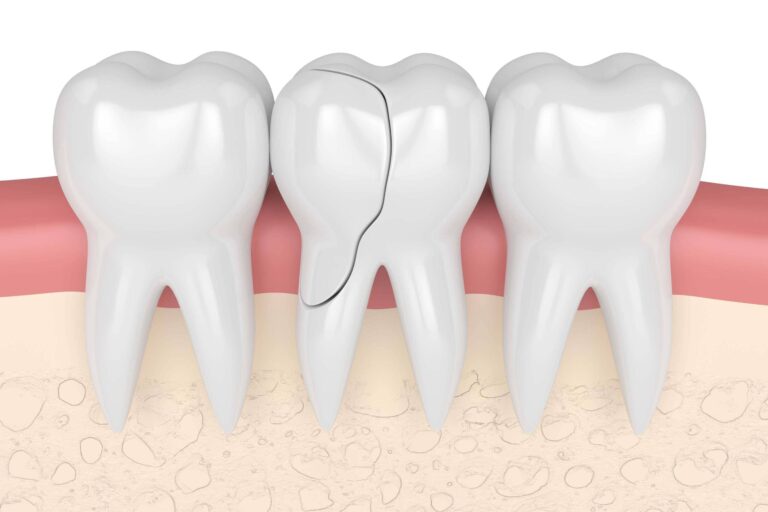
Cracks often start small, from grinding, large old fillings, or trauma.
They frequently cause intermittent pain that patients ignore.
If untreated:
Early detection saves the tooth in most cases.
Erosion, abrasion, and grinding (bruxism) slowly wear teeth down.
If untreated:
Advanced cases often require full-mouth rehabilitation rather than simple restorations.
Delaying dental care is extremely common, and it does not mean you’ve done anything wrong.
However, dental conditions do not resolve on their own. The earlier they are diagnosed and treated, the more options you have, with less cost, less discomfort, and better long-term outcomes.
If it has been some time since your last visit, or if you postponed treatment, revisiting your oral health can make a significant difference in preventing future complications.